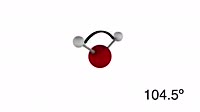
Demonstration showing the changing equilibrium of cobalt complexes in solution. Initially, the beaker contains a red-pink solution of cobalt (II) chloride, present as (Co (H2O)6) ions and chloride ions. When hydrochloric acid is added (from the left), the extra chloride ions shift the equilibrium position in favour of blue CoCl4 ions and water. The equilibrium can be sent back the other way by adding water (from the right), turning the solution pink. This can be repeated indefinitely. Many chemicals exist in equilibrium, which means that reactants are making products as fast as products are turning back into reactants. Le Chatelier's principle states that if such a system encounters a change, then the equilibrium position changes to counteract the change. Thus, as more chloride ions are added, formation of the CoCl4 ions is favoured, as this removes excess chlorine from solution. As water is added, the system moves to remove water by complexing it with the cobalt ions. This clip features the chemical equation. For a version without this text, see clip K004 2704.
Details
WebID:
C01786868
Clip Type:
RM
Super High Res Size:
1920X1080
Duration:
00:01:06.000
Format:
QuickTime
Bit Rate:
25 fps
Available:
download
Comp:
200X112 (0.00 M)
Model Release:
NO
Property Release
No











 Loading
Loading