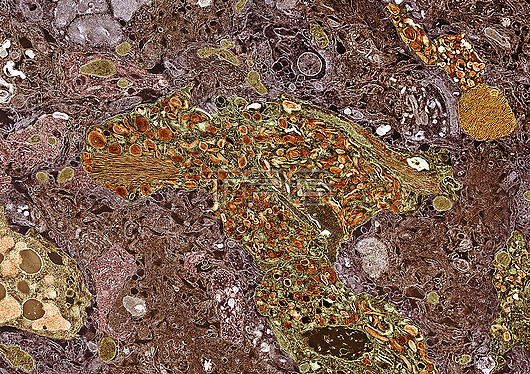
Coloured transmission electron micrograph (TEM) showing an amyloid plaque (one from centre to lower centre) in a brain with Alzheimer's disease. Amyloid plaques are insoluble aggregates of beta-amyloid protein. They are believed to be linked to Alzheimer's disease by causing nerve cell death and affecting nerve cell signalling pathways. Insoluble fibres of the protein tau, known as 'paired helical filaments' (PHF, orange stacks of parallel lines, one at centre left) are shown. Tau protein is an abundant neural protein, aggregations of which are thought to play a role in Alzheimer's disease and other neural disorders. Lipofuscin (dark spheres, lower left) are pigment granules that may contribute to the formation of amyloid plaques and the death of neurons. Magnification: x3,600 when printed at 10 centimetres wide.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP26437641
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
N/A
Property Release:
N/A
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:

 Loading
Loading