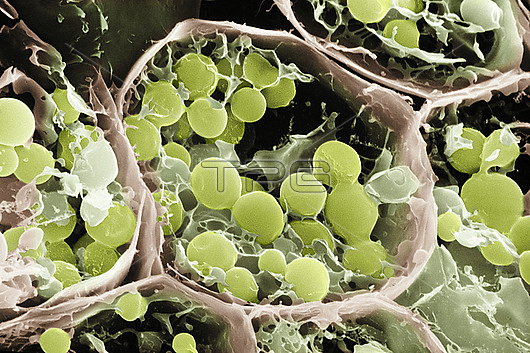
Scanning electron micrograph of the cut surface of a ripe Avocado, Persea americana. The picture shows one central cell and parts of five others. Ripe avocado flesh is comprised of about 70% water. This specimen is freeze-dried, and in a vacuum inside the microscope; it is dry. Retained are the structure of the cell walls (brown), a matrix of lamellae within the cells, and spherical particles of lipid (green). The avocado is widely regarded and promoted as a healthy food. This is due in part to the nature of the lipids (fat) that it contains.The laminar matrix is comprised mainly of mono-unsaturated fatty acids; the lipid particles contain small amounts of phytosterols, principally beta-sitosterol. Phytosterols reduce the absorption of dietary cholesterol into the intestines.Trials have shown that eating avocado can reduce the levels of LDL ("bad cholesterol") in the blood.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP26624786
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
N/A
Property Release:
N/A
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:

 Loading
Loading