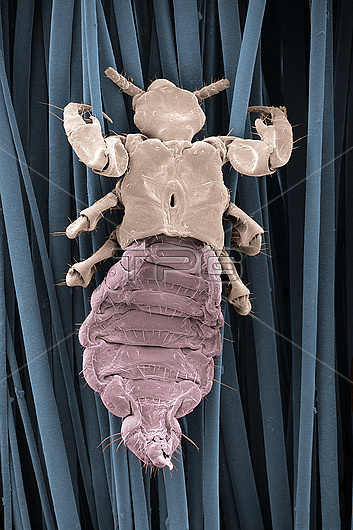
Scanning electron micrograph of a head louse, Pediculus humanus capitis, clinging to human hair. The picture shows the large front claws with an opposing "thumb", gripping the hair. The other four legs also have claws, not seen here. The segmented abdomen (below the legs) has a row of six spiracles on each side, through which the louse breathes; a pore is clearly visible on the upper two spiracles on the left. The head louse is an ectoparasite of humans; it is not known to transmit disease, but causes intense itching as it feeds on blood, and embarrassment in the form of "nits". The related body louse, P. h. humanus, lives on clothingand can transmit typhus, trench fever and relapsing fever. Head lice are mostly spread through close physical contact, rather than by shared combs, brushes or clothing. Head lice outbreaks are common in children of primary school age. Mag x 30 at 10x8
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP26537947
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
N/A
Property Release:
N/A
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:

 Loading
Loading