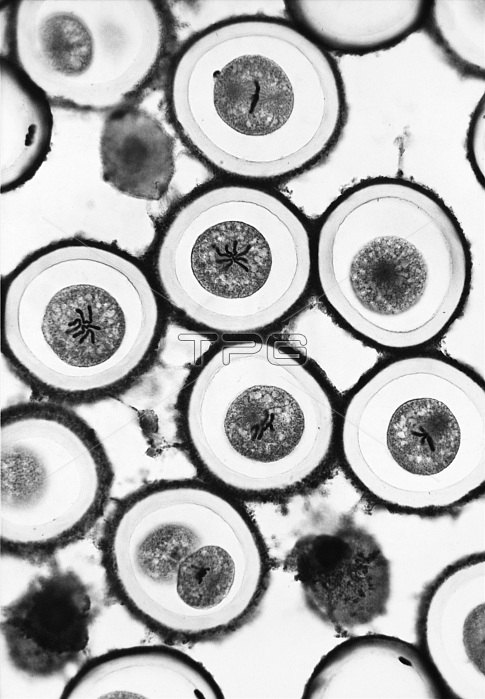
Mitosis in a roundworm (Ascaris). Mitosis is the process in which a eukaryotic cell separates the chromosomes in its cell nucleus, into two identical sets in two daughter nuclei. The process of mitosis is complex and highly regulated. The sequence of events is divided into phases, corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. During the process of mitosis the pairs of chromosomes condense and attach to fibers that pull the sister chromatids to opposite sides of the cell. The cell then divides in cytokinesis, to produce two identical daughter cells. The cycles of reproduction depend on the cycles of cell division. The ceaseless dance of the chromosomes as they duplicate and separate into new cells has two variations- mitosis for cell replacement, body growth, or sexual reproduction and meiosis for the formation of gametes. The haplolid and diploid generation in plants alternate with the rhythms of mitosis and meiosis.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP22218769
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
N/A
Property Release:
No
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:

 Loading
Loading