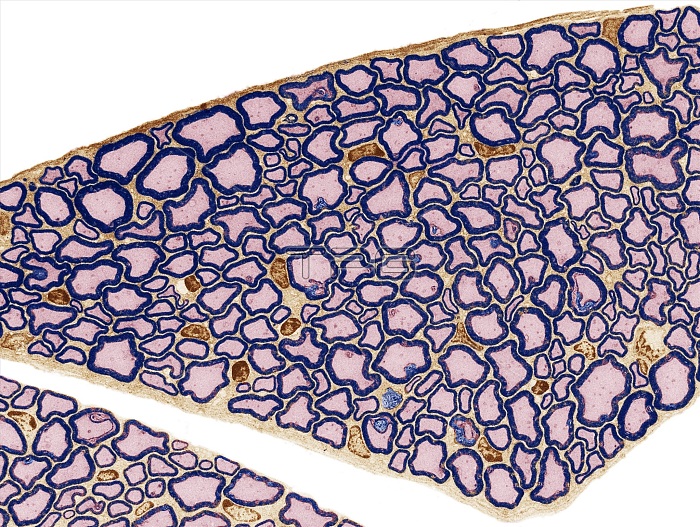
Sciatic nerve. Low power coloured transmission electron micrograph (TEM) of a section through part of the sciatic nerve. The myelin sheaths are blue and axons are pink. Myelin is an insulating fatty layer that surrounds the myelinated nerve fibres, increasing the speed at which nerve impulses travel. It is formed when Schwann cells wrap around the fibre, depositing layers of myelin between each coil. The nuclei of the Schwann cells are coloured brown. The sciatic nerve is the longest and widest single nerve in the body, going from the top of the leg to the foot. The sciatic nerve provides the connection to the nervous system for nearly the whole of the skin of the leg, the muscles of the back of the thigh, and those of the leg and foot. Magnification: x750 when printed at 10 centimetres wide.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP15939257
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
No
Property Release:
No
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:

 Loading
Loading