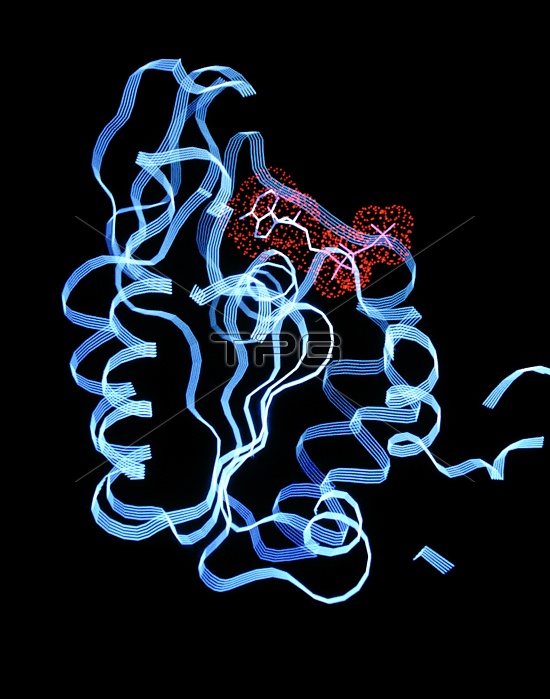
Computer graphics representation of the ATP- binding domain (reaction site) of phosphoglycerate kinase, a glycolytic enzyme (catalyst). In glycolysis, glucose is converted to pyruvate with the production of ATP: in other words, a catabolic reaction provides metabolic energy (as ATP) at the expense of the degradation of food molecules (glucose). This crystal structure is of horse phosphoglycerate kinase, a bi-lobed structure composed of two domains (one for each reactant), each composed of a six-stranded beta sheet surrounded by alpha helices (blue ribbons). Here, Van der Waals bonded ATP appears in red. This enzyme catalyses the transfer of a phosphoryl group from 1,3-diphosphoglyerate to ADP to yield ATP & 3- phosphoglycerate. Proposed mechanism involves hinge- bending to unite substrates.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP10164589
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
N/A
Property Release:
N/A
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:

 Loading
Loading